
Introduction:
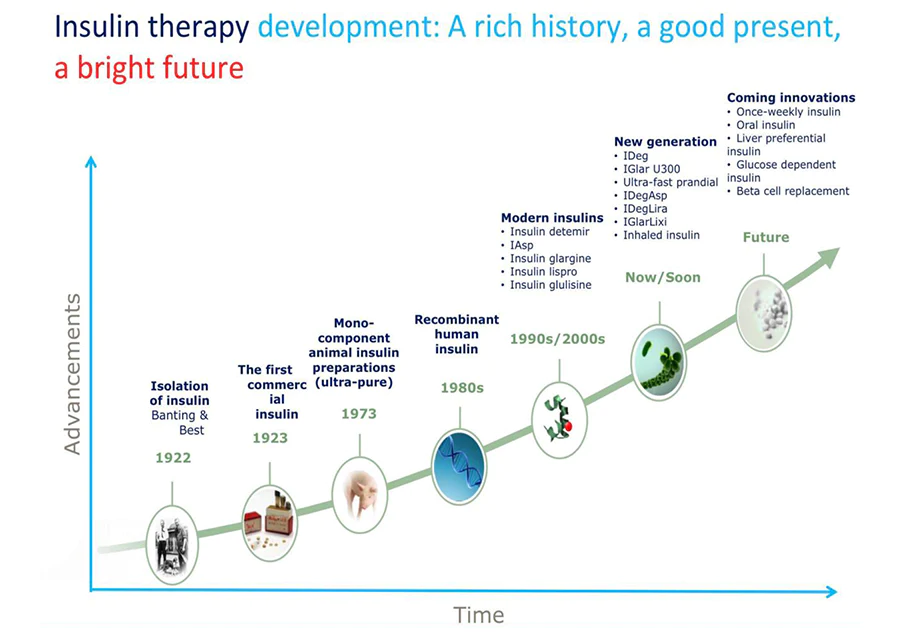
Insulin, a vital hormone produced by pancreatic islet β cells, plays a crucial role in regulating carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism. Over the years, advancements in insulin therapeutics have evolved significantly, from animal-derived insulin to the current era of recombinant human insulin. This progress has not only improved the stability and efficacy of insulin but has also paved the way for more advanced production techniques.
Evolution of Insulin Therapeutics:
The journey of insulin therapeutics began with animal-derived insulin, which though cost-effective, posed challenges such as instability and immunogenicity. However, with the advent of genetic engineering, researchers delved into the realm of recombinant insulin, marking a significant milestone in diabetes treatment. The subsequent generations of insulin, particularly the third-generation recombinant insulin, have shown remarkable advancements, notably in minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia.
The Role of Ultrafiltration in Recombinant Human Insulin Production:
The production process of recombinant insulin is intricate, involving multiple steps starting from fermentation to lyophilization preparation. Among these steps, ultrafiltration emerges as a critical technique for concentration and buffer exchange, contributing to the efficiency and quality of insulin production.
Ultrafiltration Applications:
In the realm of human insulin production from E. coli, several key ultrafiltration applications stand out:
Case Studies:
Cobetter UFELA0010010P (PES, 10kD, 0.11m2) has been instrumental in proinsulin concentration and collection. With a remarkable 98.59% product recovery rate and 96.97% water flux recovery, these cassettes exemplify efficiency and reliability in insulin production.
Cobetter UFCLA0030010P (RC, 30kD, 0.11m2) showcases its effectiveness in removing larger molecules from enzymatic cleavage insulin centrifugation supernatant. With a product recovery rate of 91.40% and notable performance in concentration and dialysis, these cassettes underscore their significance in insulin production processes.
Conclusion:
The application of ultrafiltration technology represents a cornerstone in the production of recombinant human insulin. From concentration to purification, ultrafiltration techniques enhance efficiency, purity, and yield, ultimately contributing to the advancement of insulin therapeutics and improved diabetes management. As we continue to explore innovative solutions, ultrafiltration remains at the forefront of optimizing insulin production processes, ensuring the delivery of high-quality and effective treatments to individuals living with diabetes.